For your business to thrive, improving inventory visibility is crucial. Excess inventory ties up capital, while insufficient stock can lead to stockouts and backorders, both detrimental to your operations.
Imagine a scenario where a queue of customers on your website depletes your stock faster than you can replenish it. Conversely, having an abundance of unsellable inventory can be equally problematic.
Neither situation is ideal for a business dealing with physical products. Read on to learn how to improve your inventory visibility and streamline your sales process.
What is Inventory Visibility?
Inventory visibility is the ability of a business to track its stock in real-time. This critical aspect of supply chain management involves having accurate and current knowledge of the location, quantity, and status of inventory items throughout the supply chain.
Effective inventory visibility allows businesses to monitor stock levels from raw materials to finished products across all stages, including production, warehousing, and retail.
What is the impact of a lack of inventory visibility?
“Inventory is money sitting around in a different form. And inventory management is the process of freeing that money up.”
– John W. Barlow
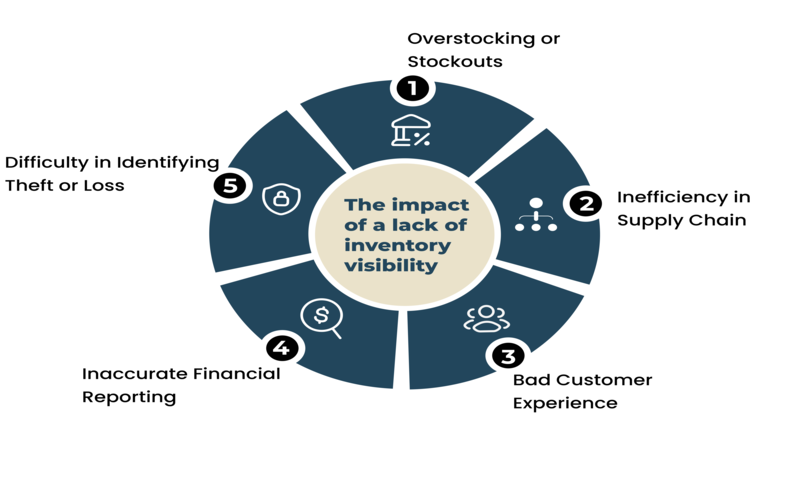
Poor inventory visibility can significantly affect various operational aspects and overall business performance. The following are some major consequences:
1. Overstocking or Stockouts
Without accurate inventory visibility, businesses risk overstocking some products while running out of others. This increases carrying costs, wastage, lost sales, dissatisfied customers, and missed revenue opportunities. Proper visibility helps you balance stock levels to meet demand efficiently.
2. Inefficiency in Supply Chain
Lack of visibility hampers supply chain efficiency, making it difficult to plan production, schedule deliveries, and coordinate logistics, leading to higher costs and longer lead times.
3. Poor Customer Experience
Customers are 2.4 times more likely to stay loyal to a brand when their problems are resolved quickly. Accurate inventory information can prevent customer dissatisfaction by ensuring products are available when needed.
4. Inaccurate Financial Reporting
Inventory value affects financial statements and is a key asset for most organizations. Inadequate visibility can lead to incorrect financial reporting, resulting in poor decision-making.
5. Difficulty in Identifying Theft or Loss
According to NRF, inventory shrinkage cost American retailers $112.1 billion in 2022, representing an average shrink rate of 1.6% of total retail sales. Without proper tracking protocols, identifying and investigating theft or loss becomes challenging, impacting sales and security.
What are the 5 challenges of inventory planning?
Inventory planning is a critical component of supply chain management but comes with its challenges:
1. Limited Visibility
Managing numerous SKUs in a large warehouse can be challenging without proper visibility, making it difficult to fulfill orders promptly.
2. Balanced Stock Controls
Finding the right balance between having enough inventory to meet demand and minimizing holding costs is challenging. Proper visibility helps optimize safety stock and reorder points.
3. Lead Time Variability
Variability in supplier lead times due to transportation delays, customs clearance, or production schedules can complicate order placement and safety stock management.
4. Inaccurate Demand Forecasting
Predicting customer demand accurately is challenging due to seasonal variations, shifting consumer preferences, and unforeseen events. Incorrect forecasts can lead to overstocking or stockouts.
5. SKU Proliferation
To serve various customer segments, many organizations offer a large variety of products and product versions. It can be challenging and inefficient to maintain a high number of stock-keeping units (SKUs), which might affect inventory planning and management. Which SKUs are profitable and contribute the most to overall sales demands rigorous investigation.
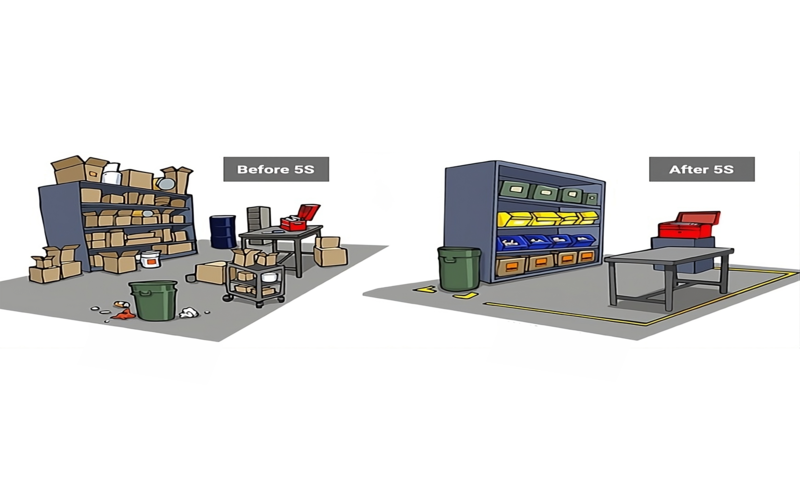
What are the 5S principles of warehouse management?
5S is a lean management strategy to utilize space effectively and maintain organized work areas. Originating from Toyota, it includes:
Sort (Seiri) – Separate necessary items from unnecessary ones, discarding damaged, expired, or obsolete items to reduce clutter.
Set in Order (Seiton) – Arrange necessary items efficiently, assigning specific locations and using labels to reduce search time and errors.
Shine (Seiso) – Regularly clean and maintain the warehouse to ensure safety, efficiency, and a productive work environment.
Standardize (Seiketsu) – Establish uniform procedures and practices across the warehouse using standard operating procedures (SOPs) to minimize discrepancies and errors.
Sustain (Shitsuke) – Maintain the 5S practices over time, with regular audits and employee encouragement to uphold efficiency and continuous improvement.
Post Implementation
Post-Implementation: Major Barriers to Warehouse Productivity
- Warehouse Layout – Effective use of space is crucial for finding inventory quickly. Inefficient layouts increase travel time, wasting time and labor costs.
- Labor Costs & Automation – Balancing labor costs with automation investments is challenging. Ensure full utilization of current solutions before adding more labor or automation.
- Inventory Visibility – Inaccurate or outdated inventory records can lead to stockouts, overstocking, and incorrect order fulfillment, reducing customer satisfaction.
- Quality Control – High pressure on warehouses can lead to errors in picking, packing, or shipping, affecting customer satisfaction.
15 KPIs for Warehouse Management
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for a warehouse are essential metrics used to evaluate the efficiency, productivity, and overall performance of warehouse operations. These KPIs help managers and stakeholders make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement.
Here are the 15 most common KPIs for a warehouse:
1 . Order Fulfillment Rate: Measures the percentage of customer orders that are successfully shipped on time and completed.
2. Order Accuracy: Tracks the percentage of orders that are picked, packed, and shipped without errors or discrepancies.
3. Inventory Turnover: Calculates the number of times inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period, indicating how well the warehouse manages stock and avoids overstocking or stockouts.
4. Inventory Accuracy: Measures the percentage of inventory accuracy by comparing physical counts to recorded inventory levels.
5. Receiving Efficiency: Evaluates how quickly and accurately goods are received into the warehouse and put away.
6. Picking and Packing Time: Measures the time taken to pick and pack individual orders.
7. Order Lead Time: Tracks the time taken from order placement to shipment, including processing and preparation time.
8. Backorder Rate: Monitors the percentage of orders that cannot be fulfilled immediately due to stock shortages.
9. Return Rate: Measures the percentage of products returned by customers, indicating potential issues with product quality or order fulfillment.
10. Space Utilization: Evaluate how effectively the warehouse uses its available space.
11. Employee Productivity: Tracks the performance of warehouse staff in terms of units picked per hour, orders processed, or other relevant metrics.
12. Safety Incidents: Monitors the number of workplace accidents and safety incidents to ensure a safe working environment.
13. Transportation Costs: Measures the costs associated with inbound and outbound transportation to and from the warehouse.
14. Order Cycle Time: Tracks the time taken for an order to be processed, picked, packed, and shipped to the customer.
15. Fill Rate: Measures the percentage of ordered items that are available in the warehouse for immediate shipment.
Regularly analyze these KPIs to identify areas for improvement and align them with company objectives.
Taking Stock
Warehouse and inventory management is a continuous task, critical for efficient operations and a positive customer experience. Proper management ensures a streamlined supply chain and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Great inventory and warehouse management = great customer experience!
Talk to our product squad: schedule a demo today!
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,








