Data leaks and cyberattacks are becoming increasingly regular these days. Businesses use customer information for an array of operations, but they also need to make sure to protect the privacy of that information, prevent data breaches, and guarantee that it is not destroyed or altered without authorization.
In addition to causing the organization significant financial losses and a permanently marred market reputation, data breaches also hurt customers.
The most recent Gartner research shows that 56% of customers frequently exhibit interest in enterprises’ cybersecurity. Customers are contacting businesses more frequently with questions about cybersecurity and potential risks associated with using their service or product.
Businesses that strive to be more customer-centric have a great opportunity of developing lasting relationships with customers by providing them with data security and keeping customer data confidential with PII encryption.
What is Personally Identifiable Information?
There are several definitions of PII or “personally identifiable information”, depending on different organizations. Going by the simplest definition, it is the information that can be used to identify a particular person in perspective.
Some examples of PII are name, email ID, phone number, address, etc.
We use and share PII at different places in our everyday lives. When we go grocery shopping at a supermarket, we provide our phone numbers, that’s disclosure of PII. When we shop online, we provide our email IDs, phone number, and shipping address, that’s disclosure of PII.
Some pieces of information are sufficient to identify an individual on their own. For example, a full name, date of birth, biometric information, social security number, and the list goes on. This is sensitive PII because such information can be used by fraudsters to commit identity theft.
While certain information is insufficient on its own to identify people, it calls for additional information to function as sensitive PII. This type of information is referred to as non-sensitive PII. Some examples of non-sensitive PII would be a first name or last name, gender, zip codes, etc.
Importance of PII Compliance
PII must be safeguarded since fraudsters can exploit information to impersonate people’s identities. Identity theft, tax fraud, cyber-attacks, and other crimes may be committed as a result of impersonation.
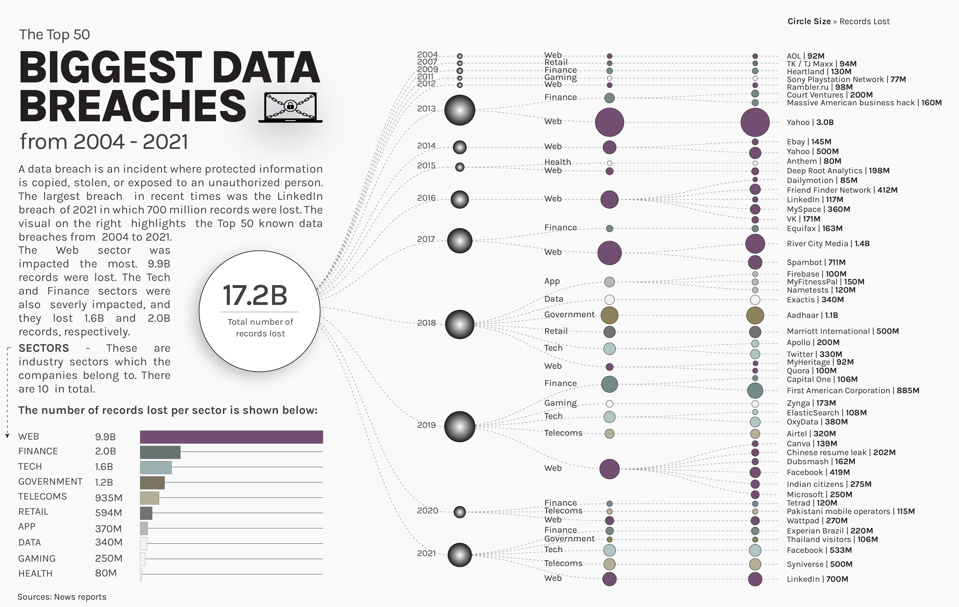
According to a study, 93% of enterprise networks can be infiltrated by cybercriminals. This itself goes to show the importance of PII compliance and keeping customer data confidential with PII encryption.
For a variety of fraudulent actions, scammers use various forms of information. For instance, opening an account on a website only requires a name and email address; yet, in order to open other accounts, such as bank accounts, additional documentation, such as birth certificates and SSNs, is required.
Not only does a breach of PII cause financial problems for your customers, but it also causes long-term reputational and legal problems for your organization. Customers typically lose trust in your business over time, which can be costly for it in the long run.
Personal data under GDPR & Difference between PII and personal data (PI)
According to Article 4 of GDPR, “personal data” means –
“Any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person (‘data subject’); an identifiable natural person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identifier such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier or to one or more factors specific to the physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural or social identity of that natural person.”
Any information pertaining to an identified or identifiable natural person is one of the definition’s major components. In other words, it refers to any information that can be used to identify a certain individual.
It might be information that is immediately recognizable, like a name, or it can be a mixture of information, such as age, job, company, city, etc. that, when put together, can be used to identify a person. (GDPR 4, undated)
But, the question is, how is PI different from PII?
Personal data under GDPR has significantly expanded the idea of PII.
The GDPR’s definition of personal can occasionally appear broader than the definition of Personally Identifiable Information in the US since the European regulation takes into account the link between personal data and an identifiable individual, which is frequently not as evident.
Protection of Personally Identifiable Information
Sensitive PII can wreak havoc if mishandled. Sometimes, the businesses that gather and store PII are unaware of the significance of appropriately handling PII. Here, we’ve covered the fundamental concept of a Data Privacy Framework and how to protect personally identifiable information properly.
Best ways of protecting PII
1 . Encryption
A strong technique to render PII useless in the hands of an attacker is data encryption. Data is protected from hackers via encryption, which makes it impossible for anybody without the proper key or password to see what is inside.
Always ensure that personally identifiable information (PII) is encrypted before it is exchanged over an insecure network or uploaded to the cloud. Use robust encryption and key management.
2. Safe deletion of old data
Are you still retaining information that is no longer required? Make sure to remove all unnecessary sensitive data to prevent fraudsters from accessing it in the first place.
3. Proper employee training and departing policies
Making sure that employees sign confidentiality agreements at all times during training and onboarding is important. They should be completely informed of the regulations they must follow when managing PII.
Ensure that their access to PII is terminated when they depart the organization. Because, regardless of how cordially the employee left the company, they might attempt to get and misuse critical information belonging to the business.
Steps to Create a Custom DPF and Adopt PII Compliance
Defining Data Privacy Framework
A data privacy framework is a standardized conceptual framework that can help businesses in safeguarding sensitive information such as credit card numbers, personal data, etc. The framework outlines how sensitive data should be defined, how risks influencing the data should be analyzed, and how measures should be put in place to secure it.
The NIST Privacy Framework and ISO/IEC 27701:2019, which extends the information security standard ISO 27001 to include a privacy framework, are two important privacy frameworks.
Every firm can and should implement its own unique data privacy framework.
Creating a data privacy framework is extremely crucial for adopting PII compliances.
More on this in the next section.
It is essential to audit all of the data your organization collects, stores, and uses to confirm that it complies with all applicable data privacy laws like GDPR, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, etc. Here is how you can adopt PII compliance accurately.
1 . Identification of stored PII
PII data may be kept in a variety of places, including servers, the cloud, or even file cabinets. Don’t forget to take into account the three states of data: in use, at rest, and in motion. This will enable you to comprehend the many systems that require protection better.
2. Classification and categorization of PII
The next step is to classify and categorize the data that has been identified. The degree to which the data can be compromised is one factor that can be used to classify information. Security should be prioritized more for some sensitive PII than for other non-sensitive PII.
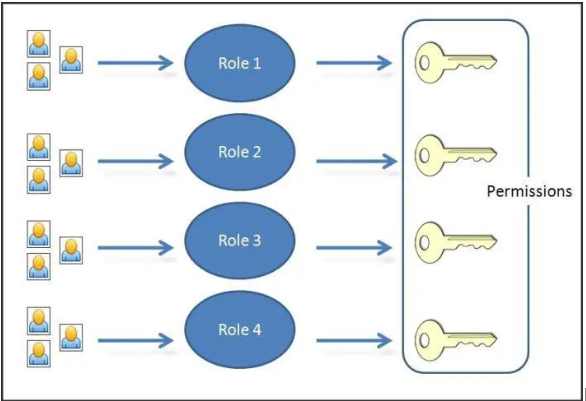
3. Policy development based on compliance
At this point, it is crucial for organizations to create guidelines for data usage, also called AUP (appropriate usage policy). These standards help employees to comprehend what data can be utilized and to what degree.
4. Data security Implementation
It is imperative that businesses put advanced data security measures in place, such as encryption, malware protection, antivirus software, etc.
6. Safe practice of IAM
Design and build a designation-based data access system. This helps in ensuring that private information is managed carefully and does not fall into the wrong hands. Additionally, it guarantees that workers only access the information they need to perform their job responsibilities and nothing more.
How to Handle PII in Customer Care?
According to a study, many security executives say they’re unprepared for the threats that lie ahead.
TechRepublic says “As cyberattacks grow in both number and sophistication, organizations are increasingly under the gun to protect themselves from compromise. Though companies have responded by upping their security budgets and adopting more advanced defenses, keeping up with the threats that will surface over the next few years will be a challenge.”
When a customer reaches out to support, they confide in them their personal information. Therefore, it is the company’s accountability of handling client information responsibly and keeping customer data confidential with PII encryption.
Customers entrust customer support with all kinds of information so that they can get appropriate resolutions. Hence, protecting their sensitive data is the very first step towards creating delightful experiences.
Here are some steps that an organization must follow to handle PII as part of customer service.
1 . Breach tests
No system is perfect. There is a good probability that your firm is storing some data that may not be compliant. It’s always a good idea to do breach tests to remove that data. Running a simulated cyberattack is one of the finest breach tests because it reveals the security system’s gaps.
2. Data Masking
Data masking is a technique for protecting sensitive data by altering the values of the data while maintaining the same format. Data masking’s main goal is to render useful information imperceptible to fraudsters while keeping it accessible to agents.
Some of the most common examples of data masking are scrambling (rearranging alphanumeric characters at random to hide the true data), and substitution (substituting a different value from a pool of reliable values in place of the original data.), variance(employing an algorithm to change dates or numbers in a column by a random fraction of their actual value), etc.
3. Gather only what is required
According to 35.9% of respondents, brands that ask for too much information make them untrustworthy.
Ask for only the details that are absolutely necessary, to win the trust of your customers. Even if a situation where customers divulge sensitive information when discussing a ticket occurs. It is not appropriate to enter that data into the system. Employees and such security procedures are crucial in companies.
4. Back up data, always!
Backing up data can shield enterprises from hardware, software, and ransomware-related data loss as well as failures that result from malicious software. For complete data protection, always ensure that your data is kept on multiple servers or data centers.
Wrap-up
Compliance isn’t the only factor in PII protection. Customer experience can be improved and communications can be expedited while safeguarding their privacy by emphasizing data security and privacy. This not only increases consumer loyalty and trust, but it also helps you future-proof your tech investments against changing requirements.
Kapture cx complies with the GDPR and the EU-US and Swiss Privacy Shield Frameworks as an international company. We continue to place a high focus on protecting the personal information of our customers, and we make sure that the information we gather is kept accurate and that we are keeping customer data confidential with PII encryption.
Talk to our product squad: schedule a demo today!
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,