Data is one of the most important currencies in today’s environment. This is because most of our online footprint is tokenized and used by businesses to sell more efficiently. This has exacerbated identity theft and data leaks. As a result, people want to know where and how their data is used.
One of the key ways to protect consumer data is to store it locally – within the nation’s geographic borders.
What Is Data Localization?
The act of physically storing a country’s data within its sovereign borders is known as data localization. This requires data to be collected, processed, and stored within the country’s boundaries. Therefore, your company might need to preserve consumer data collected overseas, in their territories. For instance, businesses are required to keep their data secure within the European Union (EU) as per the EU’s GDPR. Additionally, the data of a country’s citizens must be removed from systems in other countries before being erased from systems in their own country.
What is the difference between data localization, data residency, and data sovereignty?
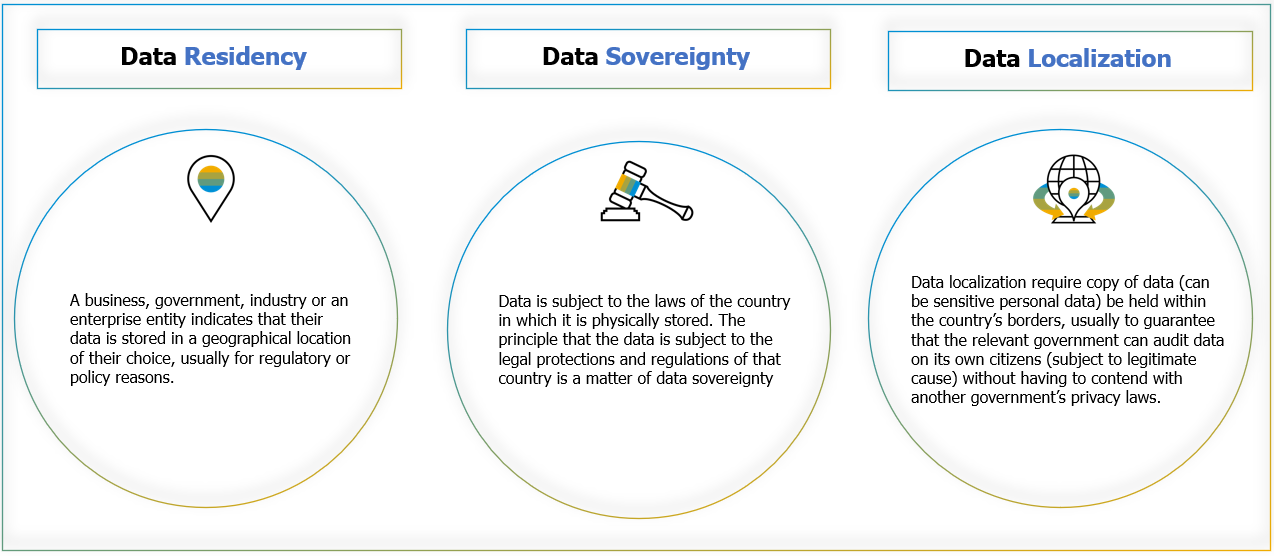
Data localization, residency, and sovereignty are related yet distinct concepts that cover how data is stored, processed, and controlled within specific jurisdictions. However, these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, making it important to understand the differences.
Data residency is the practice of a nation storing its data physically at a location whereas, data sovereignty covers the legal authority of the government over that data. For instance, the Canadian Consumer Privacy Protection Act (CCPPA) encourages greater transparency about PII data.
Residency and sovereignty are identical except that the former is based on geography and the latter, on the country’s laws.
The Advantages of Data Localization
Data localization has many advantages depending on the context, scope, and specific needs of a country or organization:-
1. Data Privacy and Security: Data localization enhances data privacy and security by keeping sensitive information within a country’s borders. This reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Data sovereignty allows a country to maintain control over its citizens’ data. This control is important where data access by foreign governments or entities could raise concerns about surveillance and privacy.
2. Faster Data Access and Processing: Storing data locally can lead to faster access and processing times, due to reduced latency in transmitting data. This can be particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time data processing or low latency, for use cases such as financial transactions.
3. National Cybersecurity: Data localization influences a country’s cybersecurity – keeping critical data within national borders makes it less susceptible to cyber threats from foreign entities. It may also simplify law enforcement and investigation efforts when dealing with cybercrimes and other illegal activities that involve data.
4. Supporting Local Economy: Data localization may promote the development of local data centers and related technology infrastructure, creating jobs and stimulating economic activity within the country. Countries need to set up numerous data centers & related infrastructure to ensure wide adoption and success of data localization.
5. Reputation and Market Standing: By upholding data protections, businesses can utilize data compliance to project themselves as credible resources and even use data compliance certifications, such as SOC2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, etc. as competitive differentiators.
At Kapture, we prioritize protecting the privacy of our customer’s data, so we adhere to all key compliance certifications.
Is data localization solely enough to ensure privacy?
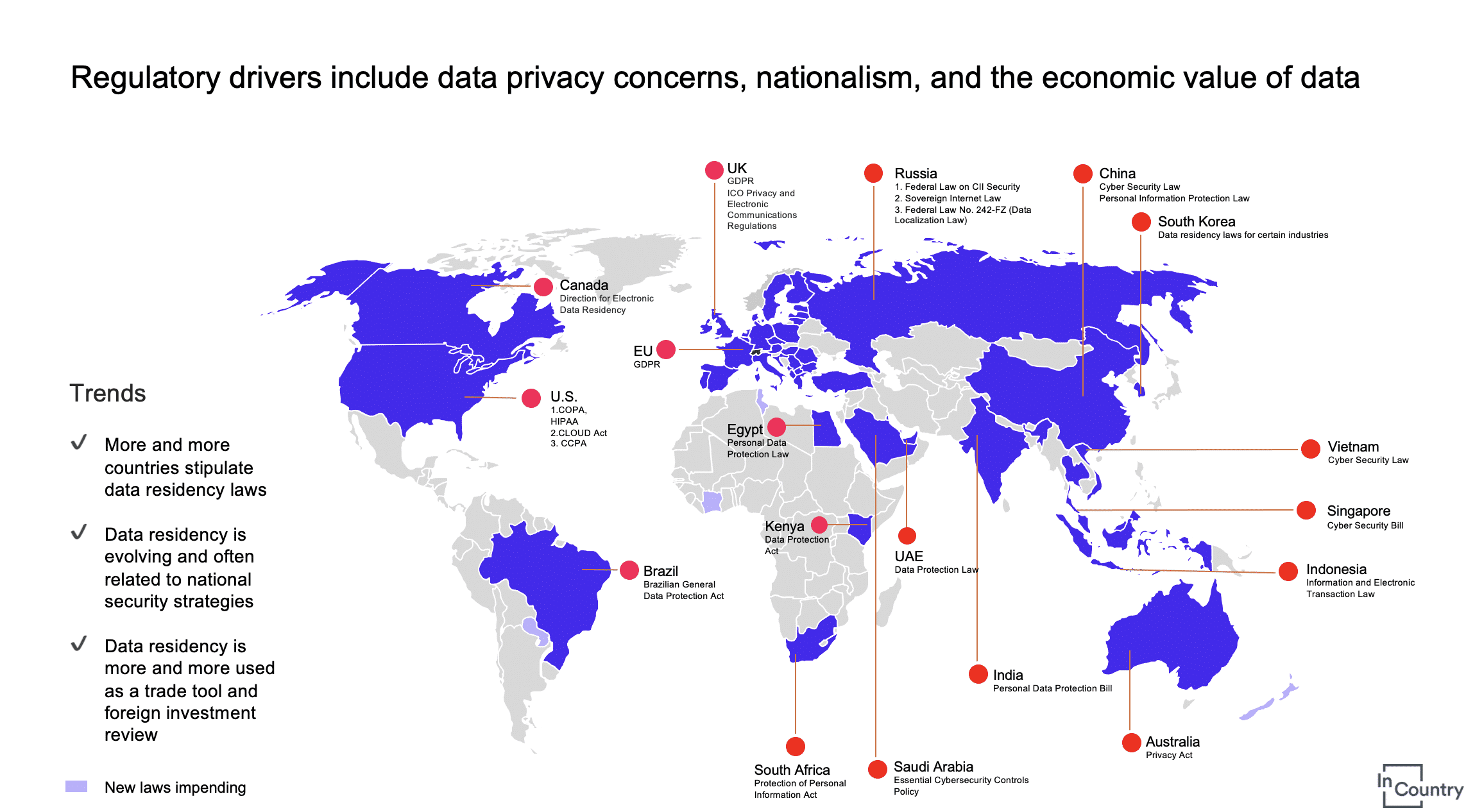
China, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan all passed new legislation or revisions to existing laws relating to data privacy requirements in 2021 alone. Restrictions on data flows are acceptable for the government to carry out its regulatory obligations or sustain security standards.
Currently, data localization regulations are in place in ~75% of nations. These regulations have significant effects on a company’s IT footprint, data governance, data architectures, and contacts with regional regulators.
Localization regulations aim to stop cybercrimes like identity theft, support local economies by generating jobs, and address growing privacy concerns. However, data localization alone is insufficient. A solid privacy framework must include effective data protection mechanisms, strong data encryption, appropriate access controls, and transparency in data management.
Wrap-Up
In the digital age, finding a balance between data protection and information freedom continues to be difficult. In order to successfully traverse the challenges of data localization, organizations must remain watchful, adapt to new requirements, and create robust data management policies as the landscape of data protection and regulations continues to change.
Want to determine if you should localize or globalize your customer data? Schedule a demo today!
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,








