Table of Contents
1. What is Qualitative Feedback?
2. Why is Qualitative Feedback important?
3. What is Quantitative Feedback?
4. Why is Quantitative feedback important?
5. How do you collect Quantitative and Quantitative feedback?
6. Quantitative vs. Qualitative Feedback in Understanding Customer Satisfaction
The customer is king and their feedback holds the key for companies to unlock exponential levels of growth. So they begin proactively collecting customer feedback which is all well and good, however, they need to better understand the nature of the feedback collected to derive actionable insights from it.
There are two kinds of feedback that can be collected: qualitative and quantitative feedback. Now the question is, what’s the best way to make use of it?
In this blog, we’ll resolve this conundrum by helping you understand the key differences between quantitative and qualitative feedback and suggest actionable ways in which you can use it to improve customer experiences
“A customer talking about their experience with you is worth ten times that which you write or say about yourself.”
― David J. Greer

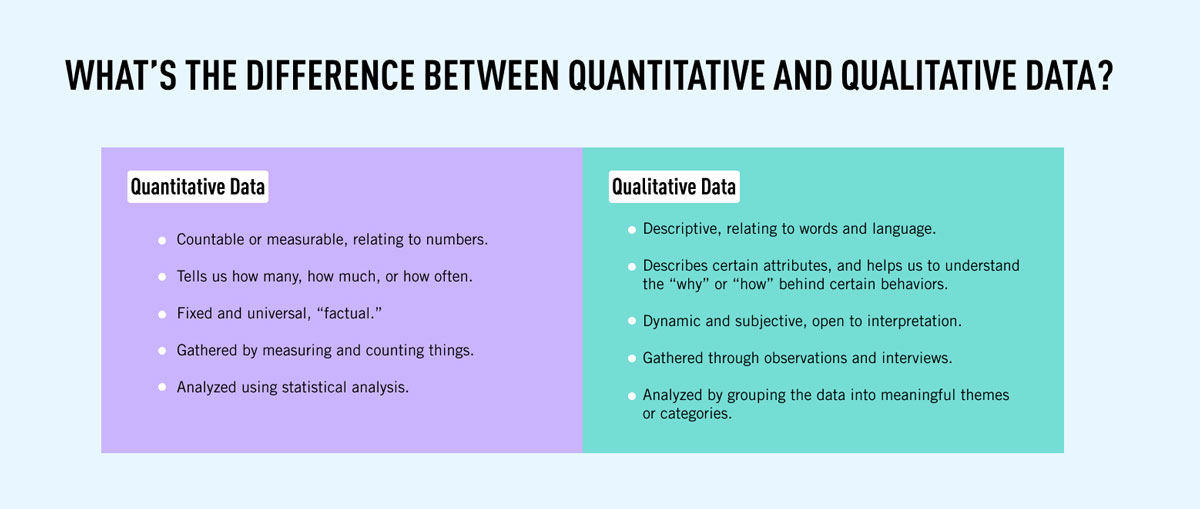
What is Qualitative Feedback?
Qualitative feedback refers to descriptive, non-numerical information about a product, service, or process. It involves subjective opinions, observations, and insights that provide a deeper understanding of the user experience or the quality of a particular offering. This type of feedback is often expressed in words rather than numbers and can come from various sources, such as customer reviews, interviews, open-ended survey responses, focus groups, and more.
Examples of qualitative feedback include comments like “The user interface is intuitive and easy to navigate,” or “I found the customer service to be very responsive and helpful.”
Analyzing qualitative feedback can be more time-consuming than quantitative data analysis, but it can be valuable for gaining a deeper understanding of user needs, preferences, and pain points.
Why is Qualitative Feedback important?
77% of consumers appreciate brands that actively seek and utilize customer feedback. Hence, the importance of collecting feedback is self-evident, isn’t it? Qualitative feedback is important for several reasons, complementing the quantitative data and offering a more nuanced understanding of a situation. Here are some key reasons why qualitative feedback is valuable:
1 . Contextual Insight:
Qualitative feedback provides context to quantitative data. While quantitative metrics offer numerical insights, they may lack the details and context necessary to understand the “why” behind certain outcomes. Qualitative feedback can offer explanations, anecdotes, and additional information that helps interpret the quantitative data.
Qualitative Feedback Example: An e-commerce company notices a drop in sales and decides to take a look at the quantitative data for answers. They find that cart abandonment rates have soared to 25%, however, this statistic doesn’t shed any light behind the reason for this spike.
However, qualitative feedback from customer reviews reveal that unexpected shipping costs at checkout are deterring customers from completing their purchases. This insight allows the company to adjust its pricing strategy to reduce abandonment rates.
2 . In-depth Understanding
Qualitative feedback allows for a deeper exploration of people’s opinions, experiences, and perceptions. It goes beyond the numbers to capture the richness and complexity of human experiences. This is particularly crucial in areas where emotions, motivations, or cultural nuances play a significant role.
Qualitative Feedback Example: A food delivery app collects user ratings on delivery times but struggles to understand why some users rate their experience poorly. By having users fill out an open-ended survey, the company discovers that while delivery is fast, customers find the app’s ETA feature misleading. This insight helps the company improve its time estimates ensuring the food arrives promptly only at the estimated time
3 . Identifying Root Causes
When faced with a problem or a challenge, qualitative feedback can help identify underlying issues. It allows individuals or organizations to explore the root causes of a particular outcome, helping them address fundamental issues rather than merely treating symptoms.
Qualitative Feedback Example: A cloud-based software company notices that there is a significant increase in customer churn when it comes to their CRM software. Their quantitative data from subscription cancellation surveys shows that “complex user interface” is a frequent reason cited. However, this response lacks depth—what exactly makes it complex?
To dig deeper, the company conducts qualitative feedback-gathering sessions with customers, including interviews and usability tests to identify the root cause of the problems. The feedback reveals that: the dashboard is cluttered with too many features, overwhelming new users and the help documentation is way too technical, for users seeking self-help to understand
Armed with these insights, the company simplifies the UI, restructures the dashboard for easier navigation, and introduces personalized onboarding tutorials. As a result, customer retention improves by 30% within six months.
4 . User Experience
In fields such as product design, service delivery, or software development, understanding user experience is essential. Qualitative feedback from users can reveal aspects of their experiences, preferences, and pain points that may not be evident through quantitative data alone.
Qualitative Feedback Example: A video streaming platform introduces a new-gen AI-powered recommendation algorithm to suggest movies and TV shows based on user preferences. The quantitative feedback (watch time metrics) indicates that users are engaging with the recommendations made, but session durations are shorter than expected.
To understand how user experience is negatively impacted, the company analyzes qualitative feedback through in-app surveys. Users here express frustration that recommendations feel repetitive, showing similar genres rather than new original content.
Armed with this knowledge, the company refines the algorithm to introduce a mix of recommendations, including trending content & user-curated lists. As a result, session durations increase by 25%, and customer satisfaction scores improve significantly.
5. Continuous Improvement:
Qualitative feedback is valuable for iterative processes and continuous improvement. It offers insights into areas that might need adjustments, improvements, or innovation. This type of feedback is often more exploratory, encouraging organizations to adapt and evolve based on qualitative insights.
Qualitative Feedback Example: A language learning app tracks quantitative data showing that users are completing lessons at a high rate, but their retention beyond the first three months is unexpectedly low.
The team initially assumes it’s due to user fatigue, but qualitative feedback from exit surveys and app store reviews tells a different story—learners feel they aren’t making real-world progress despite completing lessons.
Users mention that while the app’s structured lessons are great, they lack interactive, conversational practice that would help them build confidence in speaking. Using this insight, the company introduces AI-powered voice interactions and real-world conversation scenarios to supplement the existing lessons. As a result, user retention beyond three months improves by 35%
6. Stakeholder Engagement
Qualitative feedback engages stakeholders on a more personal level. It fosters communication and collaboration by allowing individuals to express their thoughts, concerns, or suggestions in a narrative format, creating a more inclusive and participatory environment.
Qualitative Feedback Example: A global consulting firm rolls out a hybrid work policy, allowing employees to work from home at least 3 days a week. Quantitative data from employee satisfaction surveys shows mixed reactions to this new remote policy.
To uncover the reasons behind this, HR conducts qualitative feedback sessions through focus groups and one-on-one discussions. Employees cite difficulty in scheduling cross-team meetings due to inconsistent office attendance and unclear productivity expectations for remote days, leading to them having mixed reactions to this new policy
With these insights in hand, the HR revises the hybrid work policy by defining clear remote and in-office work guidelines that clearly state to employees what’s expected of them. As a result, employee satisfaction increases by 35% and productivity remains stable across remote and in-office workdays.
7. Personalization
In contexts where personal preferences or individual experiences matter, qualitative feedback helps tailor solutions or approaches to specific needs. This is particularly relevant in customer service, education, healthcare, and other areas where individualized experiences are crucial.
Qualitative Feedback Example: A telemedicine platform offering AI-driven mental health support initially sees high user engagement based on quantitative data. However, qualitative feedback from user reviews and therapy session follow-ups reveals a major concern—the chatbot responses feel too generic and lack emotional depth.
Users express frustration that the chatbot provides standardized advice, making them feel unheard rather than truly supported. Some even report abandoning sessions due to the lack of personalized engagement.
To address this, the company takes a data-driven approach by implementing personalized recommendations based on past interactions and adding human-in-the-loop support.
As a result, user satisfaction scores increase by 40%, session completion rates improve, and retention grows as users feel more understood and supported
What is Quantitative Feedback?
Quantitative feedback refers to feedback that is measurable and expressed in numerical terms. It involves the use of data and metrics to evaluate or assess performance, outcomes, or progress in a particular area. This type of feedback is often used in various fields such as business, education, healthcare, and technology to make informed decisions and track the effectiveness of actions or strategies.
Quantitative feedback provides specific, quantifiable information that can be analyzed and compared over time. It typically involves the use of key performance indicators (KPIs) or other metrics to gauge performance against predefined goals or benchmarks.
Quantitative feedback is valuable because it provides objective and concrete information, making it easier to identify areas of improvement or success. However, it may not capture the full picture, and combining quantitative feedback with qualitative feedback (which is more descriptive and subjective) often provides a more comprehensive understanding.
Quantitative feedback is important for several reasons, playing a crucial role in decision-making and performance evaluation across various domains. Here are some key reasons why quantitative feedback is valuable:
Why is Quantitative feedback important?
1 . Measurability
Quantitative feedback provides measurable data, often in numerical form. This allows for easy comparison, analysis, and tracking of performance over time. Measurable metrics enable organizations to set clear benchmarks and goals.
Quantitative Feedback Example: A fitness application monitors when a user exceeds 10k steps daily and enables them to gauge their physical activity progress, over time periods like weeks or months. With this information in hand, it can offer tailored fitness objectives such, as boosting step counts by 5 % or incorporating interval walking exercises into the routine.
2 . Objectivity
Quantitative data is typically objective and less subject to interpretation compared to qualitative data. It reduces the influence of personal biases and emotions, providing a more standardized and consistent evaluation of performance.
Quantitative Feedback Example: A typical example of quantitative feedback is when an online shopping platform gauges customer happiness, through the Net Promoter Score (0 to 10 scale). Unlike feedback forms that are open-ended and interpretative, NPS offers a quantitative measure that allows for trend analysis, on customer loyalty and forecasting churn trends.
3 . Benchmarking
Quantitative metrics enable organizations to benchmark their performance against industry standards or competitors. This helps in understanding where an entity stands relative to others and identifies areas for improvement.
Quantitative Feedback Example: A software company analyzes its monthly active users (MAU) and compares it to industry standards. If the industry benchmark is 500,000 MAUs, but their platform only has 350,000, they can identify gaps, refine their marketing strategy, and optimize user engagement.
4. Monitoring Progress
Quantitative feedback is instrumental in monitoring progress towards predefined goals. Whether it’s financial targets, sales quotas, or project timelines, measurable data allows for continuous monitoring and adjustment of strategies.
Quantitative Feedback Example: A sales team sets a target to increase revenue by 15% in Q2. By tracking weekly sales numbers, they can monitor progress, identify slow-performing weeks, and adjust their outreach strategies to meet their goal before the quarter ends.
A sales team establishes a goal to boost revenue by 15 percent in the quarter (Q2). By monitoring weekly sales figures and analyzing performance trends over time, they can monitor progress, identify slow-performing weeks, and adjust their outreach strategies to meet their goal before the quarter ends.
5 . Data-driven Insights
Quantitative feedback provides insights based on data rather than anecdotal evidence. This is particularly important in fields like data science, analytics, and research, where statistical analysis of quantitative data leads to valuable insights.
research, where statistical analysis of quantitative data leads to valuable insights.
Quantitative Feedback Example: A ride-sharing application reviews the data on ride cancellations. It discovered that 20 percent of users cancel their trips because of long wait times. By using this information, the company adjusts its driver deployment strategy to minimize wait times and decrease cancellations
6. Accountability
Numerical feedback allows for clear accountability. Individuals or teams can be held accountable for achieving specific numerical targets or meeting performance metrics, providing a basis for performance reviews and goal-setting.
Quantitative Feedback Example: A call center tracks the average handling time (AHT) of its customer service agents. If an agent consistently goes over the target of 3 minutes per call they are assigned extra training sessions for improvement.
7. Scalability
Quantitative feedback is scalable and can be applied consistently across different levels of an organization or in various contexts. This scalability is especially important for large enterprises or projects with diverse components.
Quantitative Feedback Example: A global fast-food chain measures order accuracy across 10,000 locations worldwide. Since the same metrics apply across all locations, they can easily compare performance, identify underperforming stores, and implement operational improvements at scale.
How do you collect Quantitative and Quantitative feedback?
Always remember that a comprehensive feedback strategy often involves a combination of both quantitative and qualitative methods. This provides a more holistic understanding of the subject of interest and allows for more informed decision-making.
Additionally, selecting the appropriate method depends on the goals of your feedback collection and the nature of the information you seek. Over 40% of companies fail to recognize customer experience management as a strategic opportunity, often limiting their efforts when it comes to feedback collection. Hence, the strategy of collecting and analyzing feedback matters. Collecting both quantitative and qualitative feedback involves different methodologies and approaches. Here are common methods for collecting each type of feedback:
Qualitative feedback
1 . Surveys and Questionnaires:
Design open-ended questions to encourage detailed responses. Use a mix of closed-ended and open-ended questions to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. Consider using online survey tools for easy distribution and data collection.
2 . Interviews:
Conduct one-on-one interviews for in-depth insights. Use open-ended questions and probes to encourage participants to elaborate on their thoughts. Consider both structured and semi-structured interview formats.
3 . Focus Groups:
Bring together a small group of participants to discuss specific topics. Encourage group interaction and conversation. Use a skilled moderator to guide the discussion and ensure all participants have a chance to speak.
4 . Feedback Forms:
Create forms or cards for individuals to provide feedback. Place these forms in physical locations or within digital platforms. Include open-ended questions to capture qualitative responses.
5 . Usability Testing:
Have users interact with your product or service while you observe. Ask them to think aloud and share their thoughts during the process. Take note of pain points, positive experiences, and suggestions for improvement
Quantitative feedback
1 . Online Forms
Create web forms or online data entry points with quantitative fields. Use tools like Google Forms, Typeform, or SurveyMonkey to collect responses.
2 . Surveys and Questionnaires
Design a structured survey with closed-ended questions. Use rating scales (e.g., Likert scales), multiple-choice questions, or numerical inputs. Surveys can be administered online, via email, or on paper.
3 . Web Analytics
Utilize web analytics tools like Google Analytics to track online user behavior. Monitor metrics such as page views, bounce rates, conversion rates, and session duration.
4 . Customer Reviews and Ratings
Encourage customers to leave ratings and reviews. Aggregate and analyze numerical ratings and feedback from platforms like Yelp, Amazon, or specialized review sites.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Feedback in Understanding Customer Satisfaction
Both quantitative and qualitative feedback play important roles in understanding customer satisfaction, and each approach has its own strengths and limitations. The choice between quantitative and qualitative methods often depends on the specific goals of your research and the type of information you’re seeking.
In the context of customer satisfaction, using a combination of both approaches is often recommended. Quantitative surveys can provide a numerical measure of satisfaction levels, and qualitative methods, such as interviews or focus groups, can delve into the nuances and reasons behind those satisfaction levels. This combined approach allows for a more holistic understanding of customer satisfaction.

Wrap-up
There are no right or wrong methods for gathering and analyzing customer feedback. Always, both qualitative and qualitative feedback are important. You should achieve this by clearly defining your research questions and objectives and matching them up with your data sources and analysis techniques.
Additionally, it is crucial to gather and analyze data in a methodical manner while upholding dependability. This will help your organization expand by improving the understanding of your customer base and ultimately, the customer experience.
Talk to our product squad today!
FAQs
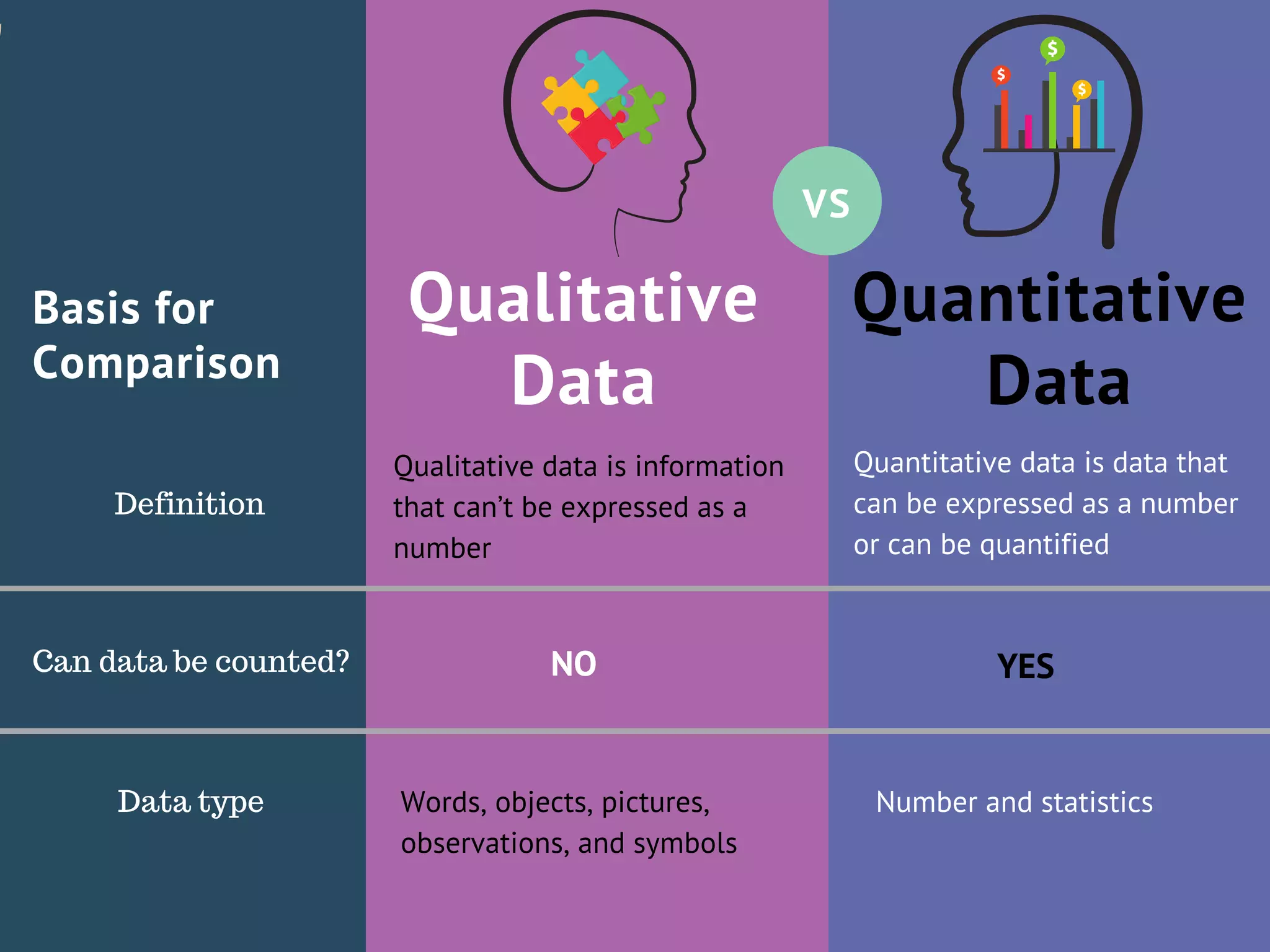
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
Quantitative data is measurable and based on numbers. Qualitative data is open-ended and based on interpretation. Both help understand customer feedback. Quantitative data answers “what” with numbers, while qualitative data explains “why” with customer experiences.
2. What is quantitative analysis?
Quantitative analysis in customer feedback involves evaluating numerical data such as survey ratings, Net Promoter Scores (NPS), and customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores to identify trends, measure performance, and support decision-making. By analyzing structured data from customer responses, businesses can track improvements, detect pain points, and refine their customer experience strategies.
3. How does qualitative feedback improve customer satisfaction?
Numbers can tell you what is happening, but qualitative feedback tells you the story behind why it is happening. By analyzing open-ended reviews left by customers and their history of past interactions, businesses can easily discern customer expectations and areas of frustration which can be rectified to meet the needs of their customers.
4. What methods provide qualitative data about customer experiences?
To gather qualitative insights, organizations use:
- Open-ended surveys – Let customers describe their experiences in their own words.
- Customer interviews – Direct conversations uncover valuable details.
- Focus groups – Discussing experiences with multiple customers reveals common themes.
- Usability testing – Observing customers interact with a product highlights pain points.
5. How can businesses collect qualitative feedback?
- Open-ended surveys – Capture detailed responses beyond just a rating.
- Direct interviews – One-on-one conversations offer in-depth insights.
- Focus groups – Identify recurring themes by engaging multiple customers.
- Customer reviews & social media – Monitor online platforms for honest feedback.
- Live chat & support interactions – Analyze real-time customer concerns.
- Usability testing – Watch users navigate products to detect friction points.
6. How can businesses collect quantitative feedback?
- Surveys & questionnaires – Use structured rating scales and multiple-choice questions.
- In-app & on-site feedback – Deploy real-time pop-ups, post-transaction, or exit surveys.
- Customer support ratings – Gather post-chat and ticket closure ratings.
- Online reviews & polls – Monitor structured feedback from social media and review sites.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) – Ask, “How satisfied were you with our service?”
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,








